It could be cheaper to build new renewables than new coal as early as 2020
Between 2020 and 2022, it could be cheaper to build new solar PV than to build new coal capacity across the three countries of study. These changing cost dynamics call into question the 70 GW or $120 bn of planned coal investments across Indonesia, Vietnam and the Philippines.
Within a decade it could be cheaper to build new renewables than operate coal
It could be cheaper to build new renewables than operate existing coal fired power plants within 10 years. By 2027/28, it will be cheaper to build new solar PV capacity in Vietnam and Indonesia than keep existing coal plants operating. By 2028/29, this will be the same for new onshore wind in Vietnam and solar PV in the Philippines. Please see the individual country briefings for detailed company results.
Stranded Risk Summary Table
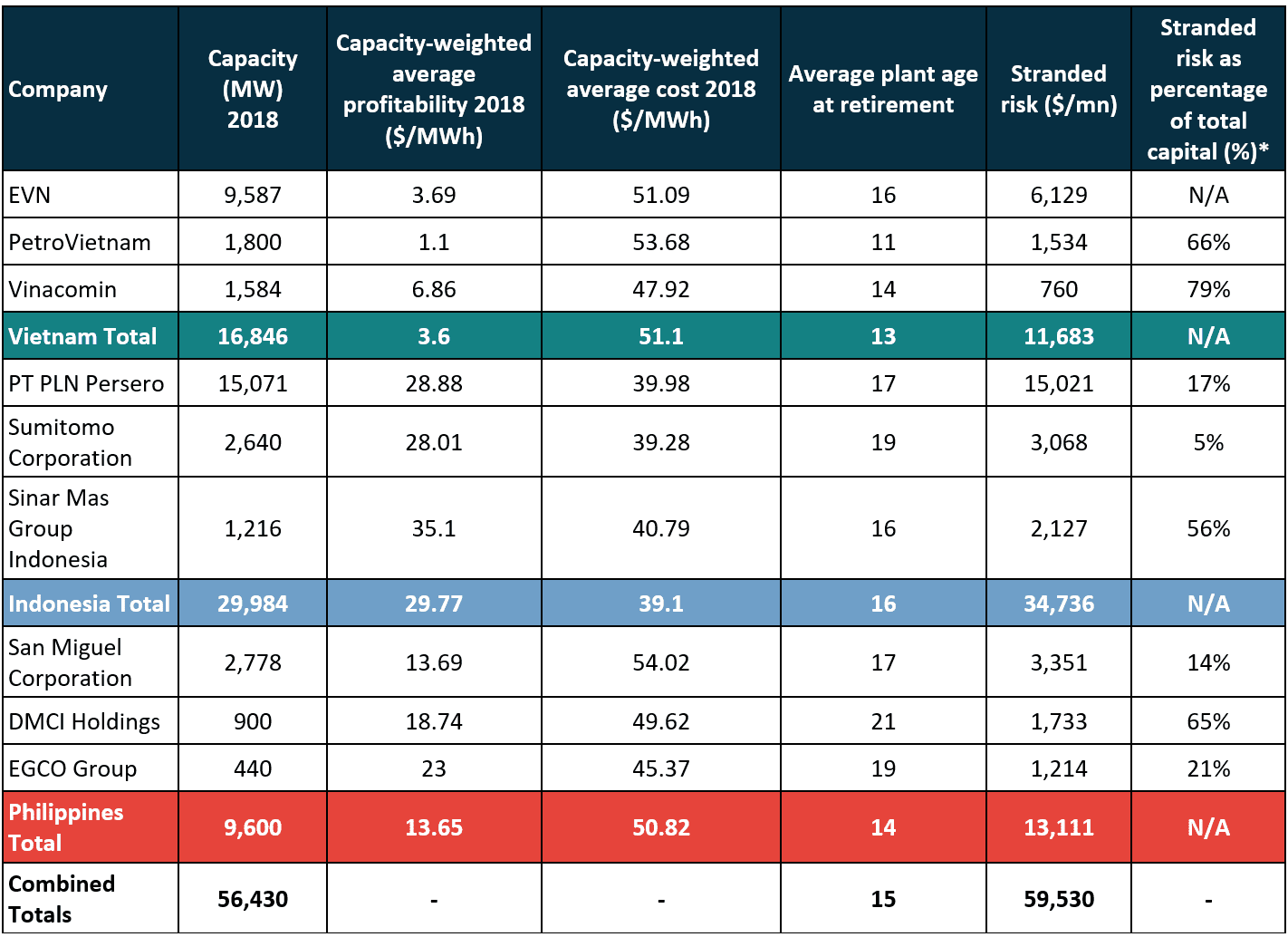
Majority of combined $60bn stranded asset risk is concentrated in existing coal capacity
Coal power owners in Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines collectively risk losing up to $60 bn in a scenario that sees coal power phased-out in a manner consistent with the temperature goal in the Paris Agreement. The average coal unit in these nations will be retired at just 15 years old, far earlier than forty-year assumptions often associated with coal plant lifetimes. Indonesia is the most at risk of stranded assets, with $35 bn at risk. Please see the individual country briefings for detailed company results.

